Fibromyalgia is a widespread disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Symptoms of fibromyalgia, which include chronic pain and fatigue, may have a major effect on a person's standard of living.
What is Fibromyalgia?
Pain and discomfort in the muscles and joints are classic symptoms of the chronic condition known as fibromyalgia. Fatigue, sleep issues, cognitive difficulties (sometimes known as "fibro fog"), and increased sensitivity to stimuli are common side effects. Although the precise etiology of fibromyalgia is unknown, it is thought to result from a combination of genetics, environment, and neurological factors.
Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Individuals with fibromyalgia may have a wide range of symptoms, however the following are among the most often reported:
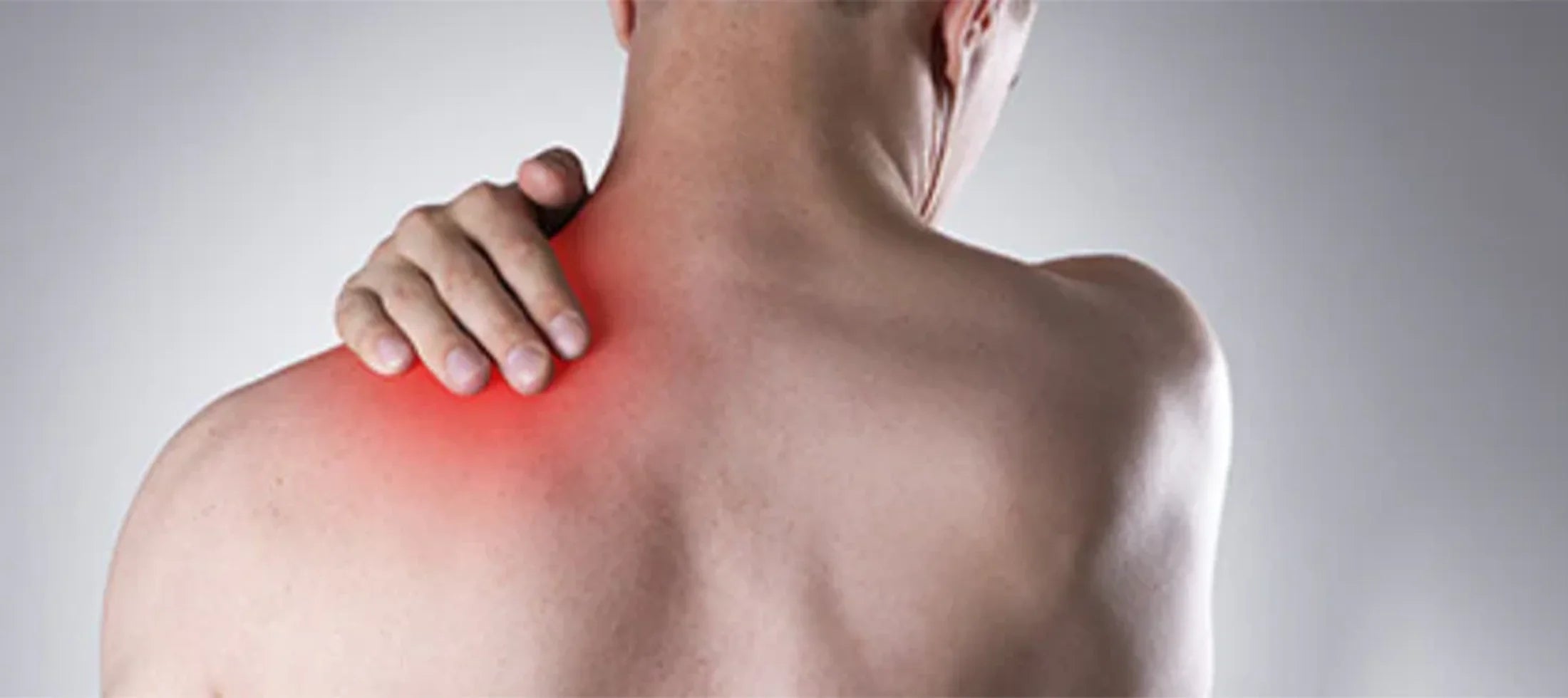
Widespread pain and tenderness: Tender spots are a common location for experiencing pain, although they may occur everywhere.
Fatigue: Fibromyalgia patients often report extreme weariness that can't be remedied by getting enough sleep.
Sleep disturbances: Sleep issues including insomnia and restless leg syndrome are common in people with fibromyalgia.
Cognitive difficulties: The inability to think, remember things, or concentrate is often referred to as "fibro fog."
Sensitivity to stimuli: One typical symptom is an increased sensitivity to external stimuli including light, sound, touch, and temperature.
Headaches: Many people with fibromyalgia also suffer from frequent migraines and tension headaches.
Causes of Fibromyalgia: It is still unclear what triggers fibromyalgia, although researchers have identified several possible causes. Some of them are:
- There is evidence suggesting that genetic factors play a role in the development of fibromyalgia.
- Abnormalities in pain processing and neurotransmitter imbalances might contribute to heightened pain sensitivity.
- Physical or emotional trauma, infections, or significant life stressors could potentially trigger fibromyalgia in susceptible individuals.
Diagnosis of Fibromyalgia: Due to a lack of conclusive diagnostic testing, fibromyalgia may be difficult to diagnose. Healthcare providers often depend on the existence of certain criteria, such as generalized pain and tenderness in at least 18 identified sensitive spots and a history of symptoms including exhaustion, sleep disruptions, and cognitive difficulties. Also, to rule out other illnesses that have similar symptoms, physicians may do blood testing and imaging.
Fibromyalgia in Females: Although fibromyalgia is more common in women, it may affect either gender. Hormonal, genetic, and societal variables may all contribute to the greater prevalence of fibromyalgia in women, while the precise causes for this gender disparity remain unknown.
Fibromyalgia Treatment: Pain relievers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants are often provided to patients to lessen their discomfort and promote better sleep.
- Symptoms may be controlled with the aid of several lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, stress management strategies, and a regular sleep routine.
- Physical therapy may aid with mobility and pain relief via the use of gentle stretching, cardiovascular activity, and focused massage.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT may help with pain management, better coping methods, and dealing with the emotional issues of fibromyalgia.
- Some people may find comfort in alternative treatments including acupuncture, yoga, and meditation.
In Conclusion
Fibromyalgia causes widespread pain, tiredness, and other symptoms. Fibromyalgia may be difficult to diagnose and treat, but knowing its symptoms, causes, and therapies can help patients manage their illness and improve their health. Consult a doctor if you suspect fibromyalgia or are experiencing its symptoms. Research into the causes and therapy of fibromyalgia gives promise for better management and quality of life.


Share:
Bipolar Disorder: Unraveling the Rollercoaster of Mood
The Effects of Regression and Anxiety